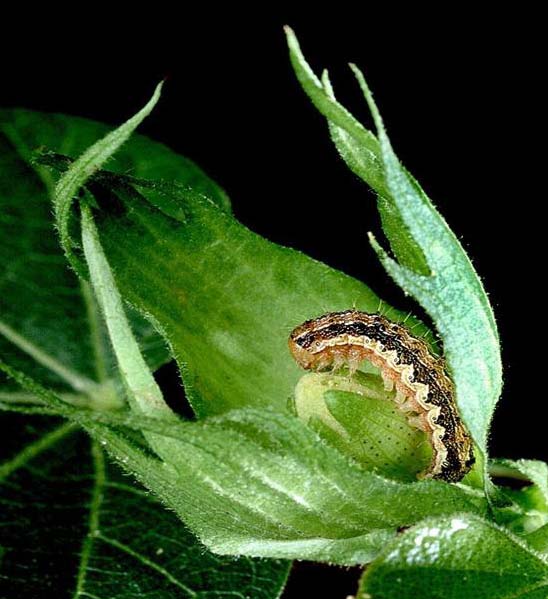
This set of presentations from the conference on Outstanding Organic Agriculture Techniques held during September 2009 at Bangalore deals with pest and disease management practices in organic farming, which rely primarily on preventive and integrated methods.
This set of presentations from the conference on Outstanding Organic Agriculture Techniques held during September 2009 at Bangalore deals with pest and disease management practices in organic farming, which rely primarily on preventive and integrated methods.
Crop production and plan protection in organic farming
This paper by S R Sundararaman presents organic farming as the only recourse for farmers, to save both livelihood and the health of the soil. Organic farming methods enable farmers save money and turn their farmyard waste into value-added products for increasing crop production. Farmers will not have to be dependent on agri-business companies for seeds, fertilizers and pesticides. Our self-reliance is thus preserved. A large portion of our country's foreign exchange is used to pay for the import of petroleum products. By going organic we will also help our country save on valuable foreign exchange. Our land will keep giving us returns for extended periods of time unlike farming as per the green revolution, where the land stays productive for a short time and then becomes sterile.
The uppermost question in the minds of farmers who have recently converted to organic farming or who want to turn organic is how to ensure that crop production does not reduce and how to protect the plants from disease, without the chemical fertilizers and pesticides that their fields have grown used to. This paper provides the answers and it also seeks to reassure all farmers that there is no farm which cannot turn around and produce quality crops in sufficient quantity, using organic farming methods.
Techniques for application of herbal repellents
This presentation by Salma Jafarali, begins with a discussion on the adverse effects of pesticides, components of Integrated Pest Management such as biological c ontrol by natural predators, cultural methods, mechanical methods, bio-pesticides and use of herbal repellents. It also deals with the selection of herbal repellents like Lantana camara, Calotropis gigantia, Jatropha curcas, Thevetia peruviana, Datura metal, Pongamia pinnata, Adathoda vasica and Carica papaya. It presents the flow chart for the preparation of EM-based natural pest repellents. Finally, it gives an account of common crop pests.
ontrol by natural predators, cultural methods, mechanical methods, bio-pesticides and use of herbal repellents. It also deals with the selection of herbal repellents like Lantana camara, Calotropis gigantia, Jatropha curcas, Thevetia peruviana, Datura metal, Pongamia pinnata, Adathoda vasica and Carica papaya. It presents the flow chart for the preparation of EM-based natural pest repellents. Finally, it gives an account of common crop pests.
Biological pest management
This presentation by M John Joseph, Tamilaga Ulavar Tholilnupta, Kalagam deals with how organic farming shows a way to minimize the hazardous effect of chemicals. In organic farming, pests and diseases are controlled naturally by using the plant extract and leaf extract of medicinal plants and by using beneficial micro-organisms (bio-control agents). It deals with bio-control agents, bio-fungal agents, bio-bacterial agents and more.
Enhancing plant defense mechanisms for disease management
This paper by Anurag, Sujata and Maya Goel of Mojo Plantation,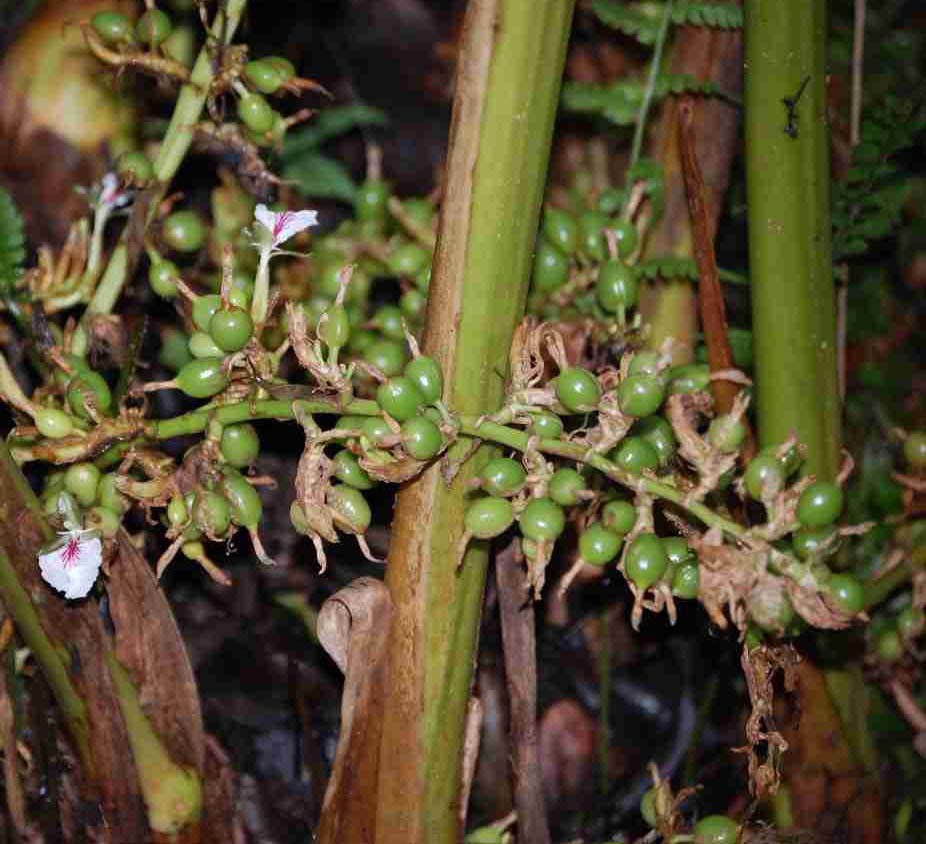 Karnataka discusses how use of chemicals and pesticides has degraded lands and water bodies all over the world. If we now find it essential to species survival, to revert back to holistic farming practices, it is imperative to understand what is happening within the plant system when it is subject to disease and other stress factors. Emulating natural ecosystems and adapting them into our farming systems has been done over the years by our traditional farming practices. There is an amazing range of methods of biological control and use of botanical materials to manage diseases in cropping systems.
Karnataka discusses how use of chemicals and pesticides has degraded lands and water bodies all over the world. If we now find it essential to species survival, to revert back to holistic farming practices, it is imperative to understand what is happening within the plant system when it is subject to disease and other stress factors. Emulating natural ecosystems and adapting them into our farming systems has been done over the years by our traditional farming practices. There is an amazing range of methods of biological control and use of botanical materials to manage diseases in cropping systems.
The presentation in the context, of tackling cardamom stem borer discusses how plant extracts like Pongamia pinnata, Annona reticulate, Ocimum tenuiflora, Nicotiana lumbaginifolia, Lantana camara and Vitex negundo can be used for pest control. It also covers traditional pest management methods such as Adathoda vasica, Acorus calamus, Alpina galangal, Azadirachta indica, Calotropis procera, Cassia fistula and Crotolaria retusa. It recommends multi-cropping at all levels, keeping cropped areas surrounded by fallow lands, encouraging weed diversity, encouraging biodiversity through resource management and minimizing sprays to nutritional and liquid manure applications.
Pest and disease management in cotton
This presentation by Alka Najan of Institute for Integrated Rural Development, Aurangabad deals with the case of pest/disease management in cotton. Healthy plants living in good soil with balanced nutrition are better able to resist pest/disease attack. The pest/disease control strategies suggested are mainly preventative rather than curative. It deals with details about the seed treatment, land preparation and inter-culture operations. It suggests the following treatment to deal with boll-worm: (a) Use of okra, cow pea, and pigeon pea as trap crops (b) Timely inter-cultural operations and (c) Destroy infested buds and flowers.
Aurangabad deals with the case of pest/disease management in cotton. Healthy plants living in good soil with balanced nutrition are better able to resist pest/disease attack. The pest/disease control strategies suggested are mainly preventative rather than curative. It deals with details about the seed treatment, land preparation and inter-culture operations. It suggests the following treatment to deal with boll-worm: (a) Use of okra, cow pea, and pigeon pea as trap crops (b) Timely inter-cultural operations and (c) Destroy infested buds and flowers.
Download all the 6 presentations:
 Techniques_in_application_of_herbal_pest_repellents_Salma_Jafarali_Agrihelp_Palakkad_OFAI_SAC_2009.pdf
Techniques_in_application_of_herbal_pest_repellents_Salma_Jafarali_Agrihelp_Palakkad_OFAI_SAC_2009.pdf Managing_insects_John_Joseph_TUTNK_Erode_OFAI_SAC_2009.pdf
Managing_insects_John_Joseph_TUTNK_Erode_OFAI_SAC_2009.pdf Crop_production_and_plant_protection_in_organic_farming_SR_Sundararaman_TNFTA_Erode_OFAI_SAC_2009.pdf
Crop_production_and_plant_protection_in_organic_farming_SR_Sundararaman_TNFTA_Erode_OFAI_SAC_2009.pdf Enhancing_plant_defense_mechanisms_for_disease_management_Sujata_Goel_Mojo_plantation_Kodagu_OFAI_SAC_2009.pdf
Enhancing_plant_defense_mechanisms_for_disease_management_Sujata_Goel_Mojo_plantation_Kodagu_OFAI_SAC_2009.pdf Pest_and_disease_management_in_cotton_Alka_Najan_IIRD_Aurangabad_OFAI_SAC_2009.pdf
Pest_and_disease_management_in_cotton_Alka_Najan_IIRD_Aurangabad_OFAI_SAC_2009.pdf Enhancing_plant_defense_mechanisms_for_disease_management_2_Sujata_Goel_Mojo_plantation_Kodagu_OFAI_SAC_2009.pdf
Enhancing_plant_defense_mechanisms_for_disease_management_2_Sujata_Goel_Mojo_plantation_Kodagu_OFAI_SAC_2009.pdf